

Solutions in Water Environment
for People and Planet



Hello, I'm Minhee Hwang.
Today, we're back with Vol. 2 of our insights into the highly anticipated and controversial topic of secondary battery wastewater, where we'll define and characterize salt wastewater and discuss the relevant legislation.
Past Saemangeum Secondary Battery Wastewater Information Insight vol.1In vol. 3 of this series, we will cover the current status of lithium wastewater treatment overseas and domestic recovery technologies, as well as the latest AI-based metal detection technology.
The literature sources are listed below and the purpose of the proposal is to improve the system since the first implementation in 2011, when the management system was implemented as of 2012.
출처 : 관련자원 – 산업폐수 “염” 독성 관리 및 공공처리시설 “염” 고시 적용방안 연구
If you're looking for a more detailed ecotoxicology management guide, check out the 2016 edition.
Ecotoxicology Management Guidebook 2016.11
In addition, the Ecotoxicity Management System has the following structure and work process.
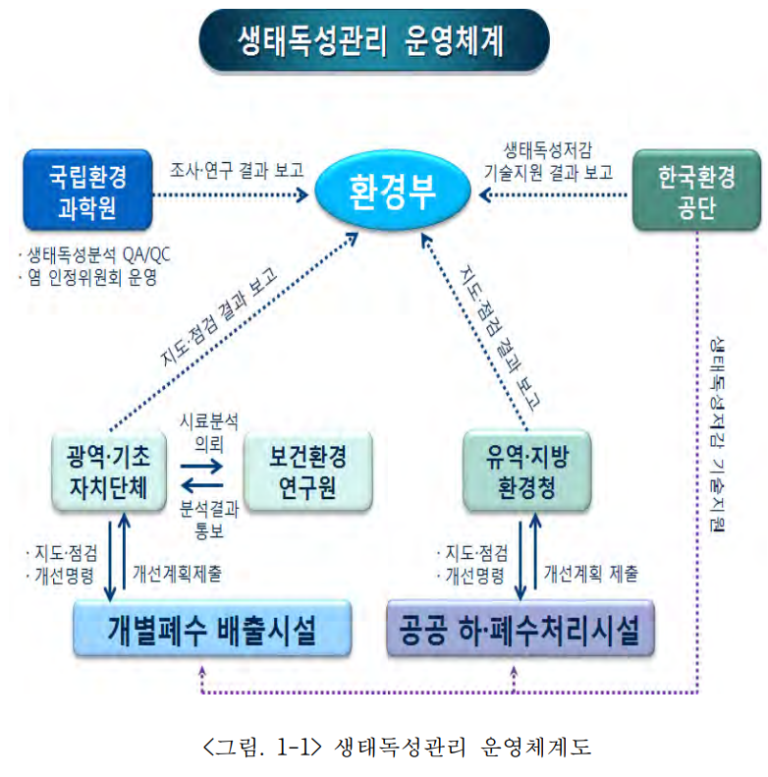
In Chinese, salinity refers to wastewater that contains salts, or substances with a salt content, and the two most problematic are sodium chloride and sulfate.
As defined by the National Academy of Environmental Sciences Legal definitionsis as follows.
“Legal definition of ”salt"When these substances are discharged into public waters in large quantities, they cause ionic imbalance problems in freshwater organisms, and the effects of salinity or ionic tension are difficult to determine, causing many problems in regulation and implementation evaluation by ecotoxicological assessment.
쉽게 풀어 쓰자면, 염분독성을 가진 화합물질로 규정되는 염화나트륨, 황산염이 담수에 유입되었을 때 생태독성을 지닌다하여 ‘생태독성을 지니는 염폐수’라 정의합니다.
This salt wastewater creates an ionic imbalance that is harmful to freshwater and aquatic life.
In addition, ecotoxicity is expressed in units of TU and has a base of 1.
그렇다면 환경부는 이 ‘염’에 대해 어떤 기준을 두고 어떻게 염을 조사하며 규제를 두고 있을까요?
In 2012, the National Academy of Sciences published a study on chlorine toxins using water fleas to help preserve healthy aquatic ecosystems.
“We selected representative facilities where ”salt” could be a problem and conducted field surveys and ecotoxicity assessments to propose management plans for "salt" in Korea, and implemented them to propose system improvements based on the results.
The “Ecotoxicity Integrated Management System” was implemented on January 1, 2011 to protect healthy water ecosystems. The operation of this system was investigated to have many problems in operation management, as "salt" was the main substance that caused the exceedance of the ecotoxicity discharge permit standard in about 401 TP3 tons of individual wastewater discharge facilities and 251 TP3 tons of public treatment facilities.
For this reason, the above study was conducted in 2012 to provide a backdrop for the proposed reforms.
“Salt” toxicity facilities and management measures were divided into individual wastewater treatment facilities and public treatment facilities.
The experiments in the above research report are summarized as follows.
대한민국은 2010년부터시험생물종인 물벼룩의 상시적인 무료 분양과 법정분석기관 담당자 기술교육을 매년 실시해오고 있습니다. 물벼룩은 담수생물로 염에 대한 측정을 실시하는 생물군으로 고도의 ‘정도관리’가 필요해 매우 중요하게 여겨지고 있습니다.
The technical training of forensic laboratories contributes to the improvement of legal practitioners' understanding of the Integrated Ecotoxicity Management System and their proficiency in testing. The status of daphnia distribution and technical training of forensic laboratories conducted so far is as follows (as of 2012)
"Article 49 of the Water Pollution Process Test Standard, Acute Toxicity Test Method Using Daphnia, specifies that healthy individuals with clear provenance of the test organism should be used to ensure the reliability of the evaluation results.
Instructions for distributing water fleas are provided below.
P.11 Regulations on the sale of bedbugs and the status of technical training in statutory organizations
“물벼룩 분양은 내부지침을 규정하여 부화 후 24시간 이내의 어린개체 (Neonate), 1회 최대 200마리 이하를 원칙으로 하며, 분양 받은 후 2개월 이내에 다시 분양 받을 수 없도록 하여 시험생물종의 무분별한 사용을 방지 하고 있다.
또한, 분양받는 자는 생태독성 분석 시설 및 장비, 실무담당자 능력 등 시험 생물종 배양과 시험조건을 충족하고 있음을 증명해야 하고, 분양 받은 시험생물종을 타인에게 양도하거나 분양할 수 없도록 하고 있으며, 시험의 결과물에는 시험 생물종의 출처를 명확히 기재하도록 하여 건강한 시험생물종 사용을 통한 평가 결과 신뢰성 향상을 유도하고 있다.”
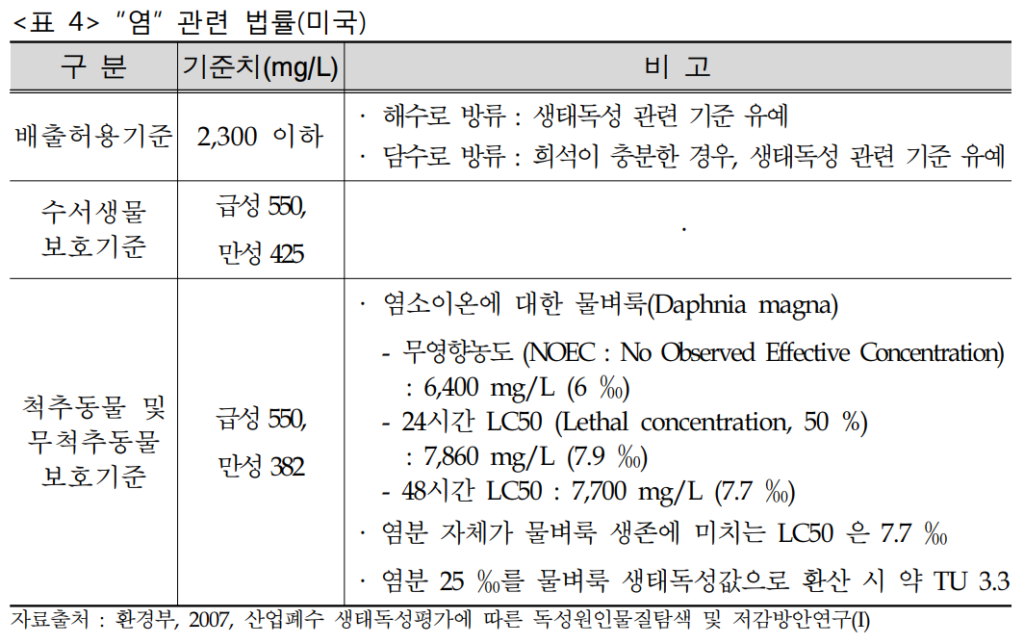
The U.S. considers salt to be an ecosystem impairment and regulates discharge limits for chloride ions (Cl-) at 2,300 mg/L. To protect public waters, it also has aquatic life protection standards of 550 mg/L acute and 425 mg/L chronic, and vertebrate and invertebrate protection standards of 550 mg/L acute and 382 mg/L chronic.
We also set pre-treatment standards for wastewater discharge facilities that indirectly discharge to public treatment facilities to ensure that the treatment efficiency of public treatment facilities can be maintained.
Here are the specific laws.
Through these laws and regulations, the United States is committed to protecting water resources and improving water quality.
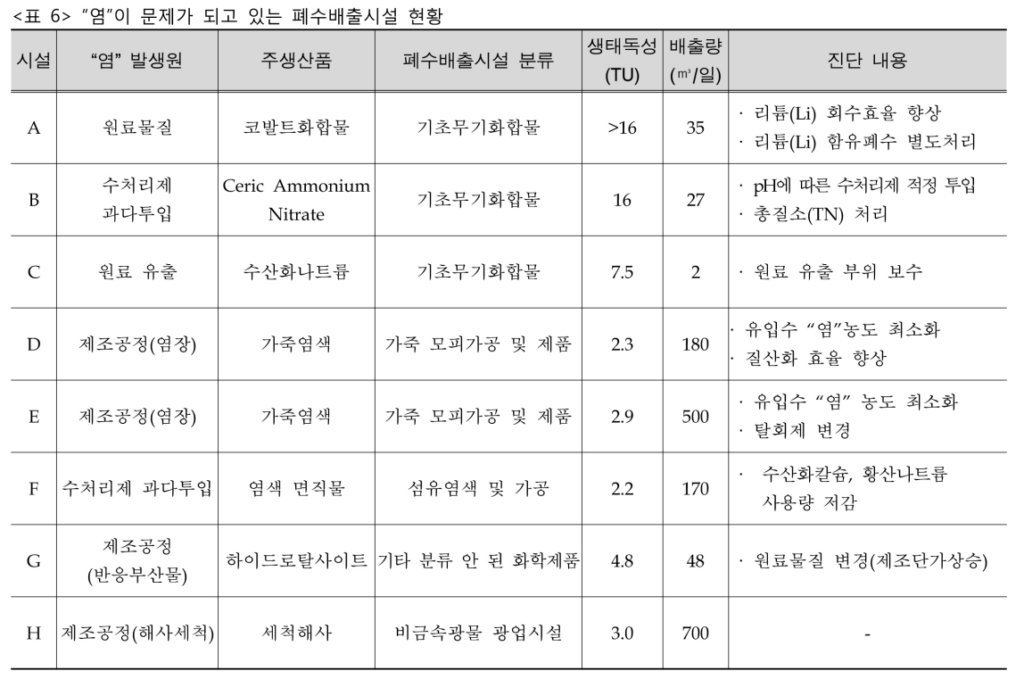
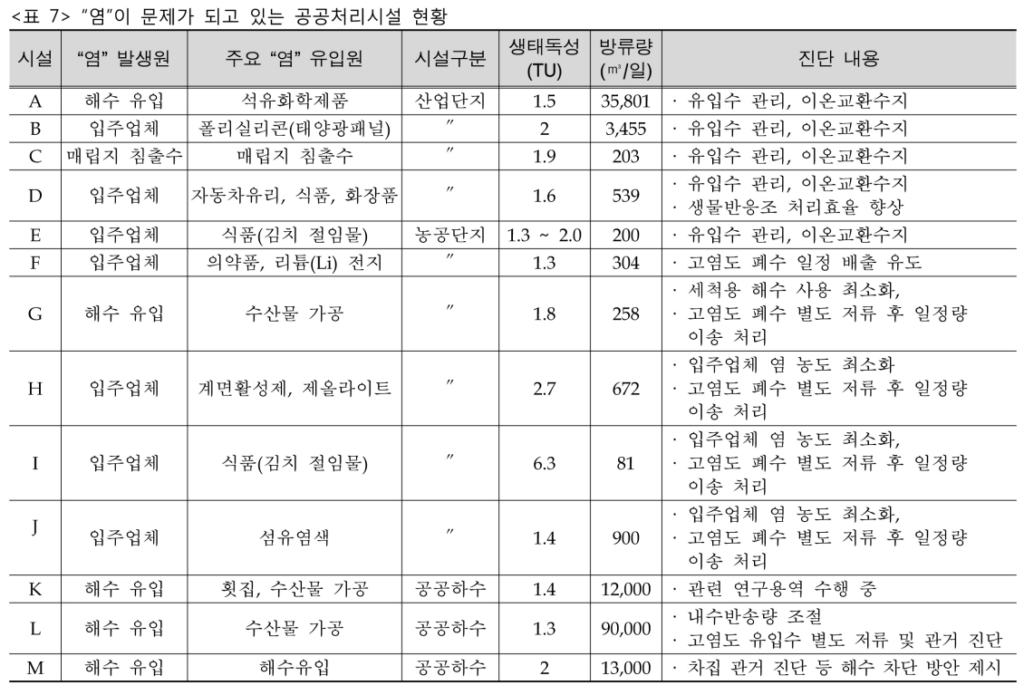
The data is from a study conducted in 2012. According to the results of wastewater discharge facilities and public treatment facilities in Table 6 and Table 7, various industries such as salt fields, marine washing, kimchi factories, dyeing factories, marine products, and solar power are generated.
As shown in the results below, the number of hazardous chemicals discharged due to the development of industry has increased dramatically, and it is practically impossible to set discharge limits for all hazardous chemicals in industrial wastewater.
P.9 Ecotoxicology Management Guidebook 2016.11
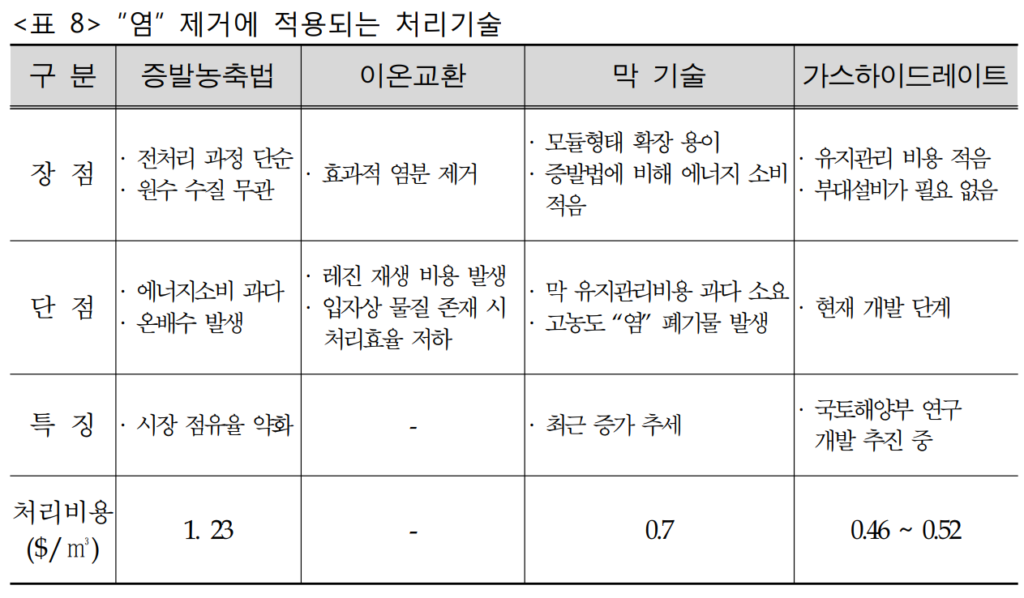
Physical and chemical treatments such as evaporative concentration, ion exchange, and membrane techniques are commonly used, but they have been found to be economically inefficient due to high initial installation and maintenance costs.

It is defined as a compound made by the anion of an acid and the cation of a base.

First, create the shape of the mixture in its natural state
Second, it is generated by the raw materials used by individual wastewater dischargers to produce their products.
Third, it is produced by chemicals used in wastewater treatment.

It is done through daphnia. Those who receive the daphnia must prove that they meet the conditions for culturing and testing the test organisms, including ecotoxicity analysis facilities and equipment, and the competence of personnel in charge, and are not allowed to transfer or sell the test organisms to others, and the source of the test organisms must be clearly stated in the test results to improve the reliability of the evaluation results by using healthy test organisms.
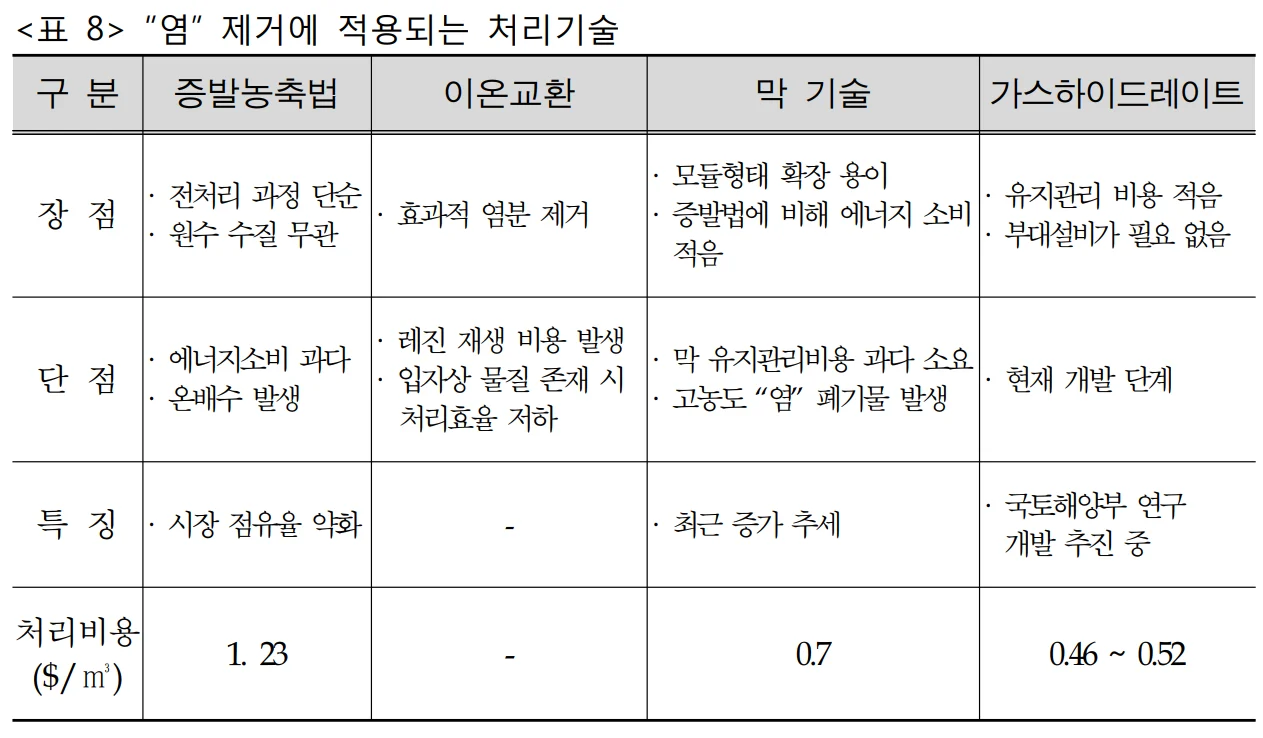
Evaporative Concentration, Ion Exchange, Membrane Technology
Gas Hydrate
The above methods are criticized for their high cost and low efficiency.
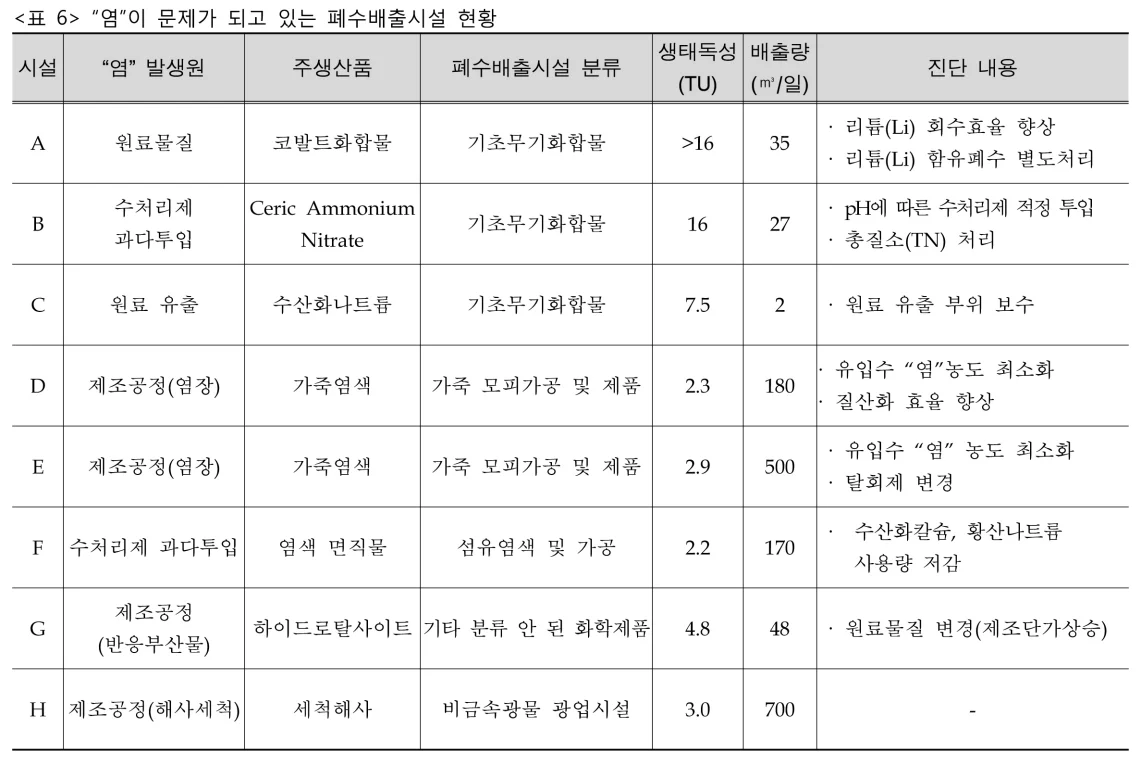
It can be caused by the input of raw materials or chemicals for water treatment in a wide variety of fields such as secondary batteries, salt plants, kimchi factories, marine cleaning, dyeing plants, etc.
Vol.1 Saemangeum Secondary Battery Wastewater Information Insight Vol.1 : View
Vol.2 What is Secondary Battery Brine Wastewater? ARK Environment : View
Vol.3 Lithium Mining and Environmental Impact Assessment - Secondary Battery Insightsvol.3 : View
Vol.4 Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) and Secondary Battery Wastewater - Background, Pros and Cons : View
Vol.5 List of domestic companies related to secondary battery wastewater treatment : View