




Hello, I'm Minhee Hwang from the public relations office of ARK. The hot topic in the Korean industry these days is the good news of private business in Indonesia and the Middle East for overseas water treatment projects, and the investment of over 1.2 trillion won by China's Longbai in Saemangeum Industrial Complex.
Saemangeum Industrial Complex is a market that is expected to attract $10 trillion in investment by the end of this year, and has been selected as Korea's second most fostered industry after semiconductors, making it a field with a bright future.
However, there is also the issue of wastewater treatment and proper regulation under environmental laws.

Despite the good news, the Saemangeum Secondary Battery Industrial Complex is also facing concerns about environmental pollution due to the lack of wastewater treatment facilities.
Secondary batteries can cause environmental pollution if they are not prepared with adequate treatment facilities and regulatory laws.
However, these are challenges that coexist with the many benefits of secondary batteries, and can be overcome with adequate water treatment and recycling.
Similarly, companies that produce or recycle secondary batteries have good intentions for the future and should focus on aligning their environmental governance with governments rather than pointing fingers.
In this regard, the Saemangeum Industrial Complex in Gunsan is concerned about the discharge of wastewater into the still inadequate wastewater treatment facilities.
As 25% in Saemangeum Industrial Complex is a secondary battery company, there is a growing interest in wastewater treatment. Of the 68 tenants, 17 are secondary battery companies, and the number is expected to increase in the future.
In China, the awareness and awareness of environmental issues has become very high, and although the country has a high level of secondary battery technology, there is also an environmental pressure to produce secondary batteries in the country.

Currently, the government and local governments are also discussing the expansion of facilities and regulation of wastewater treatment, and we will have a governance that balances development and regulation at the same time.
Secondary batteries and lithium mining, driven by electric vehicles and autonomous driving, are the most important industries of the future, while lithium battery recycling and wastewater treatment also remain significant challenges.
So let's get down to business.

Lithium secondary batteries are a business that all the big companies in South Korea are betting on producing.
The company lost the top spot in semiconductors to Taiwan's TSMC because the 3-nanometer market is no longer the limit, and processes below 3 nanometers are fraught with limitations and inefficiencies.
Superconductors, soliton particles, the ternary system, etc. have not yet appeared in the world and are not commercially available.
The semiconductor revolution has been very slow to advance to the commercialization stage unless something is discovered and invented that leads to a breakthrough in basic science, so the semiconductor market is effectively at its limit.
Due to their high power and high-energy characteristics, lithium secondary batteries are being utilized as a primary energy source for portable mobile power sources such as smartphones and laptops, as well as hybrid vehicles.
Therefore, large Korean companies are betting on lithium secondary batteries in anticipation of the generalization of electric vehicles in the future.
Lithium rechargeable batteries will undoubtedly be a key material in the future for applications such as electric vehicles and power storage, and are capable of storing and using energy continuously through oxidation-reduction reactions at the anode and cathode.
Compared to other batteries, lithium secondary batteries have advantages such as high voltage of 4V, wide application temperature of -20 to 50 degrees Celsius, high energy density of over 100Wh/kg, and high power output of over 1kW/kg, which are expected to further expand their application range.

Lithium secondary batteries use anodes and their wastewater is considered heavy metal wastewater and contains the following main substances.
Of these, the main recycling targets are oxides of transition metals, including lithium and cobalt, which are components of cathode-active materials.
Therefore, lithium and cobalt should be recycled from wastewater as much as possible, accompanied by proper wastewater treatment for the remaining heavy metals.
In particular, cobalt is a very expensive metal and is considered a grey metal, with small global reserves and limited production in certain regions. For these reasons, cobalt is not productive for secondary batteries for EVs, and other methods of secondary battery anodization are preferred.
Components of a Lithium Secondary Battery
| Separation | Components |
| Anode (Positive Electrode) | Anodic Active Materials1), Conductive Agents, Binders, Substrates |
| Cathode (Negative Electrode) | Cathodic active material2), binder, substrate |
| Separators (Separator) | Microporous polyethylene resin membrane |
| Electrolyte (Organic Electrolyte) | Lithium salts + organic solvents (LiPF6,LiBF4,LiClO4) + (EC, PC, DMC, DEC, etc.) |
| Safeguards (Safety Devices) | Safety Vent, PTC, ClD, Protective Circuitry |
Components and properties of lithium-ion batteries
A Li-ion battery is made up of four components: an anode active material, a cathode active material, a separator, and an electrolyte.
Among these components, the anode active material is the key material that determines the energy storage capacity, storage and discharge rate, cycle life, thermal stability, etc. of a Li-ion battery. Therefore, the development of anode active materials is an important area of research to improve the performance of Li-ion batteries.
The same lithium-ion battery can be categorized into different lithium-ion batteries based on the anode active material.
Newer EV rechargeable batteries are not the same as older rechargeable batteries. Here are the different types of lithium-ion batteries and their uses.
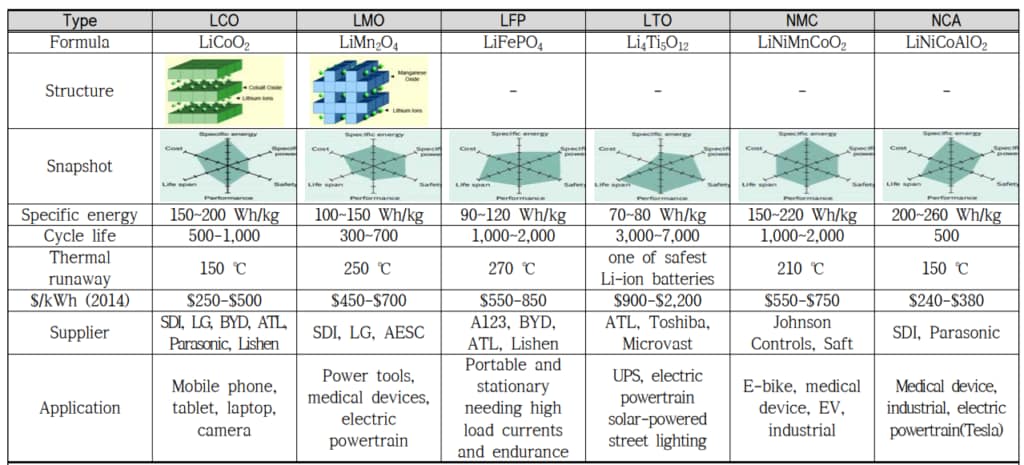
Source: Department of Resource Circulation Research, Ministry of Environment and Resources Research
Among the above methods, LMO and LFP are the most preferred anode active materials for electric vehicle batteries that require high and stable power output.
Secondary batteries for electric vehicles prioritize power output characteristics, so anode active materials are most often used for commercialization in the HEV market.
Olivine-based lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) is preferred as a cathode active material because it has a very stable structure, unlike layered cathode active materials, and has superior lifetime characteristics compared to LCO.
However, although it is competitive in safety and price, it still has problems such as low energy density to be applied to high-speed EVs, so it is necessary to further develop high-voltage olefin structure materials that replace Fe with Mn or Ni to overcome this problem.

Lithium, nickel, sulfate, cobalt, manganese, aluminum, zinc, etc.

As 25% in Saemangeum Industrial Complex is a secondary battery company, there is a growing interest in wastewater treatment. Of the 68 tenants, 17 are secondary battery companies, and the number is expected to increase in the future.

LCO method: lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2): commercialized by SONY in 1991
LNO Method: LiNiO2
NCA method: Lithium nickel cobalt aluminum oxide (LiNi0.8Co0.15Al0.05O2)
LMO method: LiMn2O4 (spinel structure)
LFP method: LiFePO4 (Olivine structure)

Iron, zinc, chromium, beryllium, barium, etc.
In the next installment, vol. 2, we will discuss the research and process of secondary battery wastewater for EVs overseas.
Vol.1 Saemangeum Secondary Battery Wastewater Information Insight Vol.1 : View
Vol.2 What is Secondary Battery Brine Wastewater? ARK Environment : View
Vol.3 Lithium Mining and Environmental Impact Assessment - Secondary Battery Insightsvol.3 : View
Vol.4 Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) and Secondary Battery Wastewater - Background, Pros and Cons : View
Vol.5 List of domestic companies related to secondary battery wastewater treatment : View